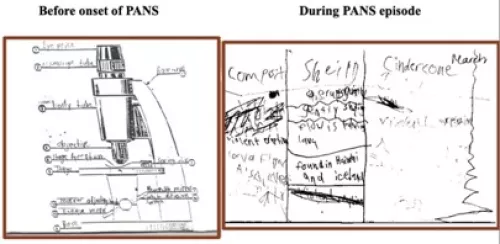
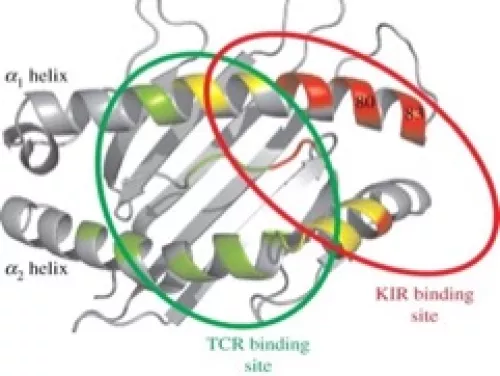
In collaboration with the Frankovich Lab at Stanford University Medical School, we are investigating HLA and KIR associations in PANS (Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome). PANS is a little-understood neurological disorder that appears to be immune-mediated as it most often occurs in patients who have had a recent, prior infection of the upper respiratory tract (Figure 1). We have performed whole MHC and KIR sequencing of over 150 PANS patients and counting. So far, we have discovered a significant association with the HLA-B locus, specifically, position 80-I which partly comprises the Bw4 epitope located on the Alpha-1 helix of HLA (Figure 2). This association prompted us to investigate the KIR3DL1 locus, which encodes an inhibitory KIR receptor on the surface of Natural Killer cells that binds the Bw4 epitope. We have found a significant association with KIR3DL1*004, a unique, misfolded protein that is mostly retained within the endoplasmic reticulum of the cell. In the future, we hope to investigate other genomic regions of the immune system in our growing PANS cohort to better understand the immunological mechanisms of this disease.
Figure 1. Drawings produced by the same patient before and after onset of a PANS episode.
Figure 2. Residues 80-83 on the Alpha-1 helix of HLA define the Bw4 epitope (circled in red).